|
STATUS:
10.23.2019
Instrument Status:
The spacecraft continues to perform nominally.
SOFIE
SOFIE returned to science measurements in October 2018, when the AIM orbit propagated to sufficiently low beta angles. The orbit is now reversed in direction compared to the previous ~12 years, so that SOFIE spacecraft sunset (sunrise) now occurs in the Northern (Southern) Hemisphere. SOFIE science and housekeeping parameters all indicate a stable and healthy instrument. SOFIE V1.3 data are available online.
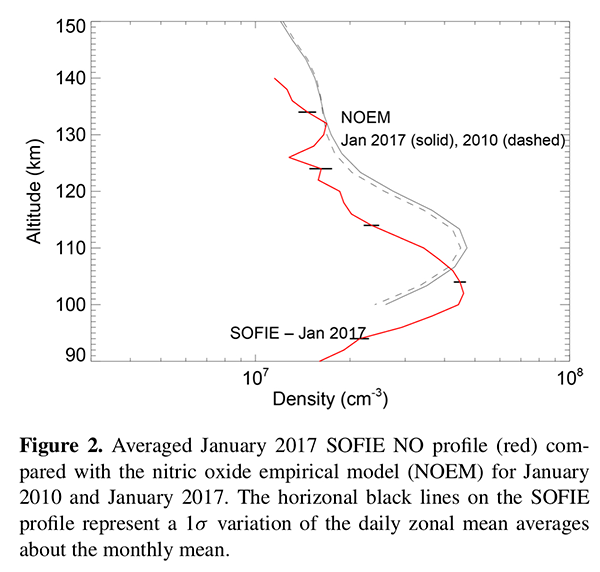
SOFIE observations were recently used with models to quantify the key dynamical and chemical factors governing the abundance and diurnal variation of lower thermospheric NO, under solar minimum conditions and low latitudes [Siskind et al., 2019]. The study also used satellite observations from SABER, in conjunction with simulations from the TIME-GCM model. This analysis was enabled by precession of the AIM orbit providing SOFIE measurements at low to middle latitudes. Two versions of the TIME-GCM were considered, the first driven solely by climatological tides and analysis-derived planetary waves at the lower boundary (free running above). The second was constrained by a high- altitude analysis from the Navy Global Environmental Model (NAVGEM) up to the mesopause. SOFIE was also compared with a NO climatology from the nitric oxide empirical model (NOEM). Both SOFIE and NOEM yield peak NO abundances of around 4 × 107 cm−3; however, the SOFIE profile peaks about 6–8 km lower than NOEM (see figure). This difference is likely a local time effect, with SOFIE being a dawn measurement and NOEM representing late morning and/or near noon. The constrained version of TIME-GCM exhibits a low-altitude dawn peak, while the model that is forced solely at the lower boundary and free running above does not (see figure). This difference was attributed to a phase change in the semi-diurnal tide in NAVGEM, causing the descent of high NO mixing ratio air near dawn. This phase difference between the two models arises due to differences in the mesospheric zonal mean zonal winds. All versions of the TIME- GCM overestimate the absolute NO abundance. Tuning the model to yield calculated atomic oxygen in agreement with SABER helps this, but is insufficient. The TIME-GCM furthermore underestimates the electron density (Ne) as compared with the International Reference Ionosphere (IRI) empirical model. This suggests a potential conflict with the requirements of NO modeling and Ne modeling, since one solution typically used to increase model Ne is to increase the solar soft X-ray flux, which would, in this case, worsen the NO model–data discrepancy.
Siskind, D. E., Jones Jr., M., Drob, D. P., McCormack, J. P., Hervig, M. E., Marsh, D. R., Mlynczak, M. G., Bailey, S. M., Maute, A., and Mitchell, N. J. (2019), On the relative roles of dynamics and chemistry governing the abundance and diurnal variation of low-latitude thermospheric nitric oxide, Ann. Geophys., 37, 37-48, https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-37-37-2019. (article)
|
